Lesson 1 Counting Subatomic Particles
Atom is the smallest particle of an element which retains the properties that define the element
neutrons are a small dense center of an atom containing protons and neutrons
electron cloud is a region surrounding the nucleus containing electrons and mostly im empty space
atomic number is number of protons. atomic number is on the bottom on the periodic table, and defines what the element is.
in a neutral atom there are the same amount of protons as electrons
number of protons and neutrons in a nucleus is the mass number, so formula for mass number is protons + neutrons
number of neutrons is found by mass number - atomic number.
an ion is an item with charge, in an ion the number of protons is not equal to the number of electrons.
if an ion is positively charged it is a cation or if negatively charged it is an anion
to calculate overall charge: overall charge = protons - electrons
Hyphen notation - Copper-65 is copper so look up the atomic number for copper on the periodic table, and 65 is the mass number, so that’s protons + neutrons, so you now have the number of neutrons too.
Lesson 2 Isotopes and Average Atomic Mass
Isotopes are atoms of the same element with the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons, meaning a different mass number.
Average atomic mass is the weighted average of the masses of all naturally occurring isotopes. Equation is : ( %abundance isotope one * mass isotope one ) + ( % abundance isotope 2 * mass isotope 2 ) + ( %ab… etc ) the % abundance must be converted to decimal form, so 58% is .58 .
Lesson 3 Nuclear Chemistry
nucleus contains protons and neutrons, which together are called nucleons
A stable nucleus holds together well, an unstable nucleus decays. an unstable nucleus is also considered radioactive.
it is called transmutation when an element changes into another element via nuclear reaction
Types of radioactive decay:
Alpha: atomic number decreases by 2 and mass number decrease by 4. low penetration power.
Beta: Atomic number increases by 1 but the mass number stays the same. medium penetration power.
Gamma: no change but lots of penetration power
Positron: Atomic number decreases by 1 but the mass number stays the same.
Symbols:

Nuclear bombardment is hitting the element with neutrons. All elements higher than uranium are made this way. Symbol:

Neutron Capture: one or more neutrons collide with an unstable atomic nucleus and make an atom that is heavier.
Lesson 4: Half life Calculations
Half Life is the time required for half of the amount of radioactive atoms to decay. 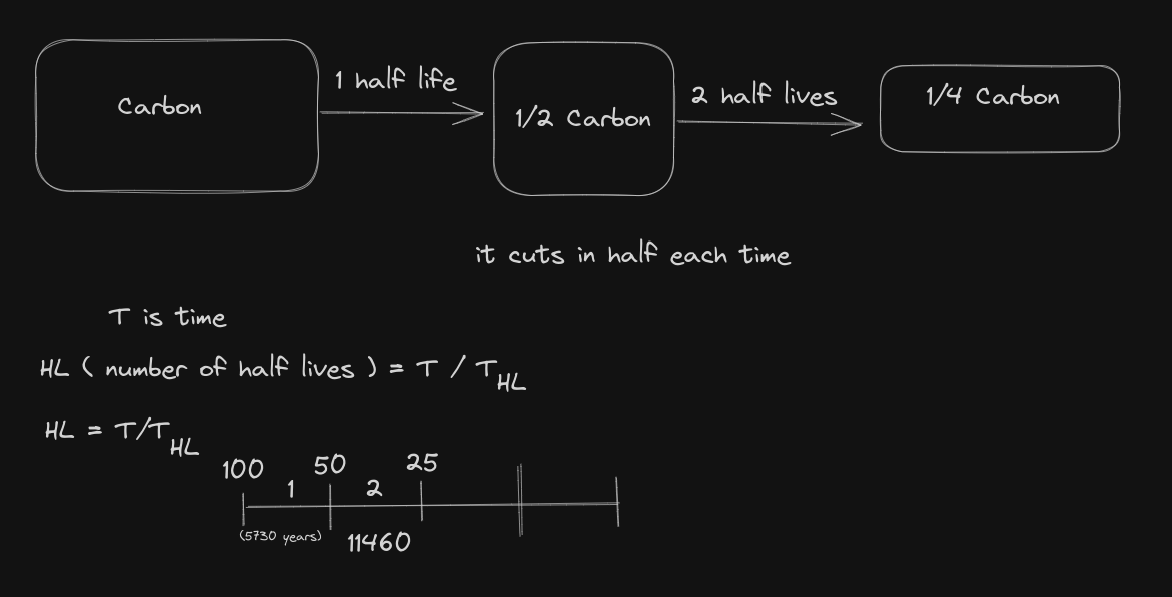
Lesson 5: Properties and Changes
Physical property: Can be determined or measured without changing the atoms or molecules of a substance’s identity
Chemical property: Can only be determined or measured as the substance changes into different substances
Physical Examples: color, texture, density, volume, hardness, malleable, brittleness, odor, boiling point, solubility, mass, anything with a phase change
Chemical Examples: Burning / Combusting, Rusting, Rotting, Flammability, Reactivity, Neutralization, Decomposing
Physical change: change in which the chemical structure of the substance is not changed but will look different. Does not produce new substances.
Chemical Change: Change in which the chemical structures of the substance are changed. Also known as a chemical reaction. Does produce new substances.
Physical Changes: breaking dissolving distilling cutting and changes in state: boiling, condensing, melting & freezing
Chemical Changes: Burning, metabolizing food, rotting, oxidation or reduction, reacting with oxygen, rusting.
Possible indicators of a chemical change : GOPEC
Gas production ( bubbles )
Odor Change
Precipitate formation ( an insoluble substance formed from 2 soluble substances )
Energy Change ( evolution of heat and light )
Color Change