Objects are really just pointers - they point to locations in memory
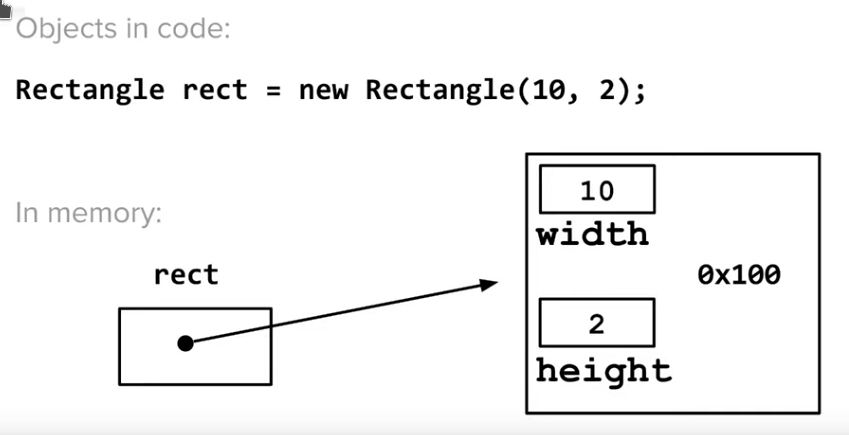
with primitives we can just use to compare if int x and int y then we can do x y because variable points to location with objects, we cannot use == , as that just would compare the memory addresses of those two objects, not their values.
to compare objects we use .equals()
compares values in each object to see if all the values stored in the objects are the same.
this is called logical equality
classes often have their own equals method
we can use == or != to determine of they are aliases of one another
Aliases
- An alias is when 2 object references are both referencing the same object
- Example:
- Rectangle rect1 = new Rectangle(10,3);
- Rectangle rect2 = rect1
we can compare objects to the keyword null to tell if an object actually references another object ( used to prevent errors )