What is a Bond and Types of Bonding
Bonds glue atoms together - forces of attraction of valence electrons do the holding together. bonds form to create stability. Atoms are most stable when they are full of valence electrons ( 8 ). exceptions to needing 8 are: hydrogen(2), lithium(4), beryllium(4), boron(6), and helium(2).
3 types:
- Ionic ( m to nm )
- covalent ( nm to nm )
- metallic ( m to m )
Ionic Metals lose their valence electrons ( cation ) & nonmetals gain valence electrons ( anion ).
There is a transfer of electrons from a metal to a nonmetal.
Covalent, they share electrons. 2 identical nonmetals that evenly share electrons form nonpolar covalent bonds, and 2 different nonmetals that unevenly share electrons form polar covalent bonds.
Metallic, they are bonded as a network, a “sea of electrons”. electrons are free to move throughout the structure.
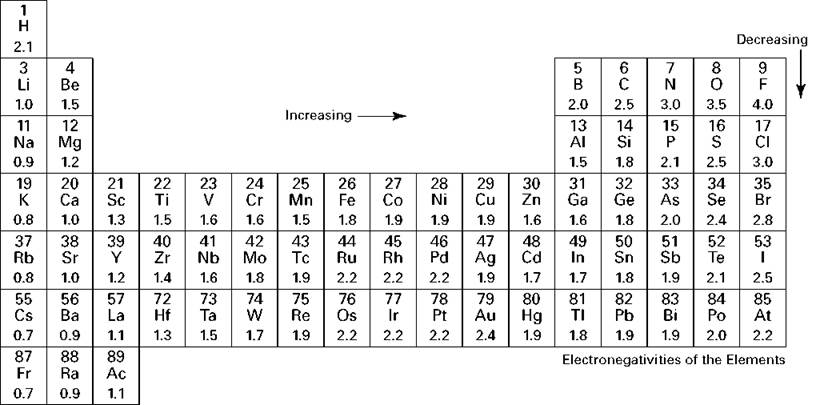
you can use electronegativity to predict bond type:
- 0 - 0.40 = nonpolar covalent ( indentical nms )
- .41 - 1.69 = polar covalent ( different nms )
-
1.70 = ionic (m/nm)
if a bond is polar, we use a polarity arrow to reflect the difference in electronegativity. the more electronegative element is partially negative and the least electronegative is partially positive.

Physical Properties of Bond Types
Ionic compounds ( ionic bonds ) have very high melting / boiling points, as they are hard to pull apart. form hard brittle solids. strongest force of attraction.
Metals have high melting points as well but vary, all are solids except Hg, strong forces of attraction.
Polar Covalent bonds have low melting points, and weak forces of attraction. Soft or liquids under normal conditions.
Non-polar Covalent bonds have the lowest melting points, weakest forces of attraction, and form liquids or gasses.
ionic compounds are soluble in polar solvents like water and insoluble in nonpolar solvents. Metals are insoluble in water. Covalent compounds vary in solubility. Like dissolves like. Polar dissolves polar, nonpolar dissolves nonpolar.
metals can conduct electricity due to the free moving electrons in BOTH solid and liquid state
ionic compounds only have free floating ions when dissolved in water, aqeuos form or when melted
covalent compounds do not have charges free to move and therefore cannot conduct electricity in any situation. exception: polar covalent molecules of acids and bases can.
ionic compounds form a lattice framework, alternating positive and negative ions closely packed together.
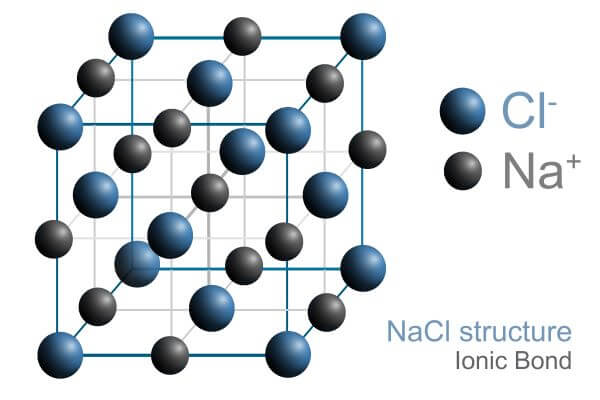 - example of this lattice framework ^
- example of this lattice framework ^
metals are represented as a framework of atoms packed with a sea of electrons.
covalent compounds form neutral seperate discrete molecules.
Drawing Lewis Dot Diagrams - Covalent Compounds
Central atom - atom on the inside of the molecule Terminal atom - atom on the outside of the molecule
Binding pair - pair of electrons shared by two atoms. form the bond.
lone pair - pair of electrons not shared - only one atom “counts” them, found on the oustide of the atoms.
steps to draw:
- find the total number of VEs
- arrange atoms and connect them
- always C never H
- subtract the number of electrons used in bonding above
- with remaining, place lone pairs around each terminal atom bonded to the central atom to satisfy the octet rule
- if any electrons remain, assign them to the central atom
- if short of a full octet on the central atom, move lone pairs from a terminal atom to a bonding pair between that atom and the central atom, forming a multiple bond.
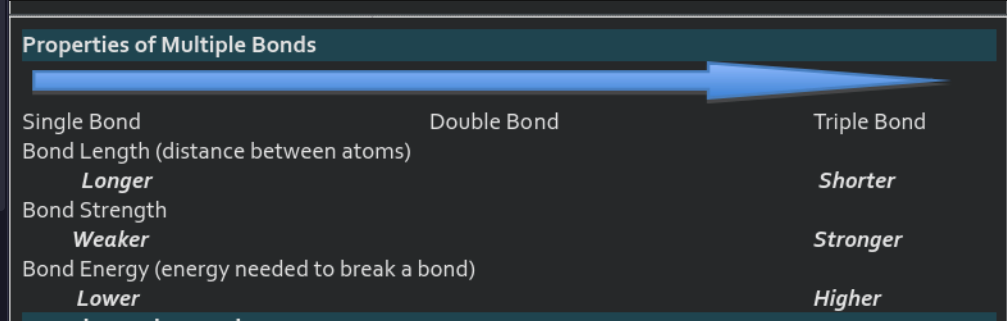
double and triple bonds are needed when there are not enough electrons to complete an octet around all atoms.
as you go into double bonds and triple bonds, the bonds get stronger and shorter.
 polyatomic ions are a group of atoms bonded together that have an overall charge. Follow same rules as before but add the numer of electrons of the negative charge or subtract the number of electrons of the positive charge to the total number of valence electrons.
polyatomic ions are a group of atoms bonded together that have an overall charge. Follow same rules as before but add the numer of electrons of the negative charge or subtract the number of electrons of the positive charge to the total number of valence electrons.
VSEPR Theory - predicting shape of a Molecule
VSEPR stands for Valence Shell Electron pair Repulsion Theory
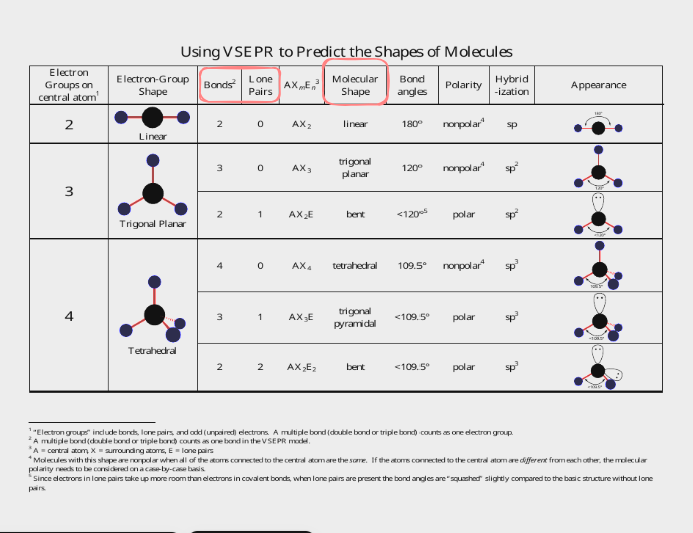
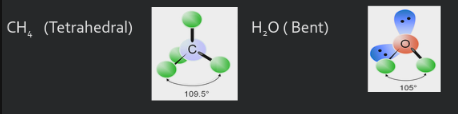
you need a good lewis drawing before you can figure out shape. when looking for shape look only at center atom. if there is no center atom, because you have only 2, it is always linear, and you also dont need to find bonding and nonbonding because its linear. when you have more than 2 you are counting bonding domains and bonding groups. you are looking to see where the electrons are, you dont particularly care if it is a double bond or single or tripe, it only counts as one bonding domain.
 lone pairs are electrons too, and must be taken into account when determining molecule shape since they repel the other bonds as well. ONLY take into account lone pairs around the CENTRAL atom, not the outside ( terminal ) atoms
lone pairs are electrons too, and must be taken into account when determining molecule shape since they repel the other bonds as well. ONLY take into account lone pairs around the CENTRAL atom, not the outside ( terminal ) atoms
lone pairs arent controlled by a nucleus ( positive charge ) on both sides, but only on one side. this means they “SPREAD OUT” more than a bonding pair.
They distort the angle of the molecule’s bonds away from the lone pair.
Predicting Polarity of a Molecule
The more electronegative part gets a δ- and the less electronegative part gets a δ+. Use an arrow pointing towards the negative side with a plus tail at the positive atom. the arrow represents a dipole: a force created due to a separation of charge within a molecule between 2 seperate atoms. It is caused by a significant difference in electronegativity.
bond polarity:
if the bond is polar you draw a dipole arrow.
molecule polarity:
if the terminal atoms ( outside atoms ) are all the same, and there are no lone pairs on the center atom, then it is NON POLAR. otherwise it is polar.
if terminal atoms are the same: symmetrical compounds that contain polar covalent bonds are NON POLAR MOLECULES. the dipoles cancel out.
dipoles must move in equal but opposite directions in order for the forces to cancel and the molecule to be nonpolar.
not eveyr molecule that has a polar bond is polar itself. if the polar bonds form dipoles that cancel out due to geometry, the molecule is overall nonpolar.

Intermolecular forces and properties
Intramolecular forces are forces WITHIN the molecule ( intermolecular forces are the bonds ). breaking them is a chemical change.
intermolecular forces are forces that occur between SEPERATE MOLECULES. breaking them is a physical change. they take less energy to break than intramolecular.
types:
- London dispersion forces
- primary thing done between nonpolar molecules and noble gases. are found between all molecules.
- weakest of the intermolecular forces because molecules cant form all the time
- larger molecules = more london dispersion forces.
- in london dispersion forces, figuring out the stronger one is a matter of counting electrons. whichever has more electrons is stronger.
- dipole dipole forces
- primary force between polar molecules.
- stronger than london dispersion
- poles are shown as δ- and δ+
- Hydrogen Bonding
- H is FON
- only between polar molecules that contain a hydrogen atom connecting with F, O, or N.
- very strong because F O N are all very small highly electronegative atoms. strongest of all intermolecular forces.
- Network Covalent Bonds
- covalent bonds called network bonds
- stronger than ionic bonds
- extremely high melting points
bond strength ranking ( strongest to weakest ) : ionic, metallic, covalent, hydrogen, dipole, london dispersion
number and strength of IMF affects properties of the substance
energy required / absorbed to break IMFs
from solid to liquid - some imfs broken
from liquid to gas - remainder broken
requires energy. called the Endothermic process.
stronger IMF means harder to evaporate melt or boil.
like dissolves like - polar dissolves polar, nonpolar dissolves nonpolar.
