Algorithms are a step by step process that solves a problem
Criteria for a good algorithm :
- Correctness
- Efficiency
- Easy to understand for anyone else
correctness just means the algorithm should work as intended
efficiency is important because effects program speed and program cost
processing time is the amount of time the computer spends processing program instructions
A computer has a limit to its CPU usage at any given time - the usage refers to the % of the cpu that is currently being used to run or process computer programs
task manager lets us monitor how our computers are using cpu processing time and usage ( xfce4-taskmanager or btop++ )
Codehs is incredibly slow and it is their fault
An efficient algorithm is one that makes economical use of processing time and computer memory
The major questions we want to ask are: How long does it take to perform this task Is there another aproach that will get the answer more quickly
Which algorithm is more efficient? #1 You say your birthday and ask if anyone in the room has the same birthday as you if anyone has the same birthday they say yes
#2 You tell anika your birthday and ask if she has the same birthday. If she says no you tell matt your birthday and ask if he has the same birthday. You repeat this process for every person in the room
#3 You only ask questions of Anika who only asks questions of Matt who only asks questions of Isabella, and so on. You tell anika your birthday and ask if she has the same birthday; if she says no youa sk her to find out if matt has the same birthday
anikas asks matt and tells you his answer, if he says no you ask anika to have matt find out about isabella anika asks matt about isabella etc
#1 is the most efficient algorithm you only ask the question once
You need to make an educated guess about the space and time needed to execute an algorithm
the absolute running time of an algorithm can’t be predicted because of a number of variable things
Statement Execution count - count the number of times a statement is exected by the program
executed statement might refer to :
- An arithmetic operation ( *, /, +, etc )
- an assignment ( int value = 2)
- a test ( x == 0 )
- a input / output
int sum = 0; // 1
int n = 10; // 2
for ( int i = 0 ; i < n ; i ++ ) { // 2+n+1
sum += i;
}
System.out.println(sum); // 2 + n + 1 + 1 Execution count total is 3 + n where n is the value initialized in the for loop while tracking individual statements is relatively straightforward, control flow statements can make this process more difficult
if you have if then else statements - only one of the statements will end up executing if you have for loops then the code repeats a fixed number of times, if it is a standard ++ increment the execution count is n - initial for nested or loops its (n - initial) * (m - init2)
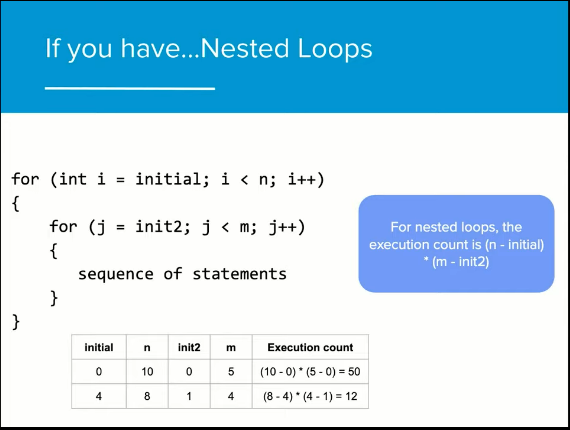
generally the algorithm with the lower execution count is the algorithm that is more efficient - as it takes less lines of code to process
What is the execution count for this program
for ( int n = 50 ; n > 0 ; n = n / 2 ) {
System.out.print(n);
//50
// 25
// 12
// 6
// 3
// 1
// execution count is 6
}what is the execution count for this algorithm
for ( int i = 0 ; i < 10 ; i ++ ) {
if ( i == 2 ) {
i ++ ;
}
// 0 1 2 4 5 6 7 8 9
// execution count 9
}break statements are more efficient than letting a loop run forever