int[][] gradeBook = {exam1, exam2, exam3, exam4, exam5}
Arrays can store arrays
int[][] gradeBook = new int[2][5]; gradebook[0] = exam1; gradebook[1] = exam2;
Arrays that store other arrays are 2D arrays.
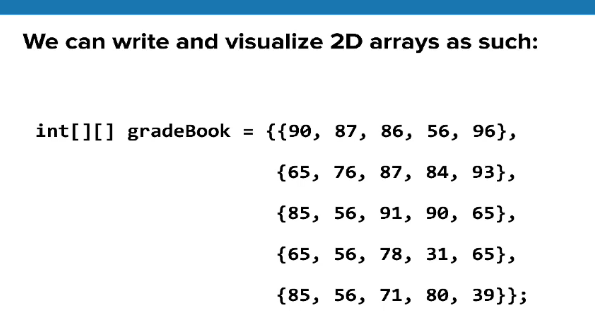
Rows are the different exams. the columns are the individual students in the gradebook if we wanted to find the exam score for a particular student, we can do so in a similar value to how we search for values in a 1D array
int grade = gradebook[2][1]
we are accessing the 3rd exam and looking at index 2
so thats
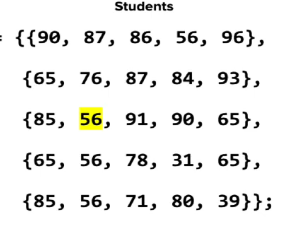
We access gradeBook[row][column]; we can use the same notation to modify element values: gradebook[3][0] = 45; row 4, first element ( 64 ) is turned into 45
523 + 6534