Name: Thomas McElroy
Molecular Model Lab
Procedure:
-
Column 1: Identify how many valence electrons are in each molecule.
-
Column 3: Draw the Lewis Dot diagram for each molecule, making sure that not only are the correct number of electrons present but that each atom has an octet. (H is exception with duet)
-
Column 4: Identify the number of Bonding Domains (# of bonded atoms off the central atom) and Non-Bonding Domains (# lone pair off the central atom) of each molecule. HINT: If a 2 atom molecule, it will have 0 bonds and 0 lone pair since there is no central atom.
-
Column 5: Using the number of domains, predict the VSEPR shape of the molecule. Remember ALL 2 atom molecules are linear.
-
Construct a ball and stick model for each molecule using the kit. Does the predicted VSEPR shape match the shape of the model you just made? It should match!
-
Column 6: Re-draw the Lewis Structure in its correct shape & draw in the dipole arrows for all polar bonds within the structure. Note: Nonpolar bonds will not have a dipole arrow
-
Column 7: Predict the polarity of each molecule. Write in POLAR (P) or NONPOLAR (NP)
-
Column 8: Predict the predominant Intermolecular Forces between each molecule (LDF, Dip-Dip, H-Bond)
| Column 1 | Column 2 | Column 3 | Column 4 | Column 5 | Column 6 | Column 7 | Column 8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| # of Valence Electrons | Chemical Formula | Lewis Dot Diagram (do all atoms except H have an octet?) | Number of Domains off Central Atom | Name of VSEPR Shape | Redraw Lewis Structure in its Correct Shape (if needed) | Polarity of Molecule P or NP | Strongest Intermolecular Forces present |
| 2 | H2 |  | Bonding: 1 Non-Bonding: 0 | linear | NP | InterMF: LDF | |
| 8 | HBr | 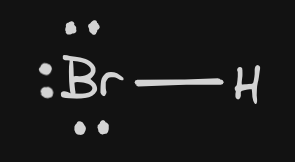 | Bonding: 1 Non-Bonding: 3 | linear | P | InterMF: DIP DIP | |
| 8 | H2O |  | Bonding: 2 Non-Bonding: 2 | bent | P | InterMF: H bonding | |
| 8 | PH3 | 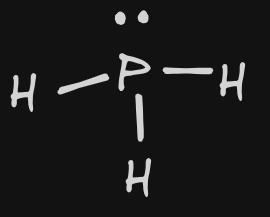 | Bonding: 3 Non-Bonding: 1 | trigonal pyramidal | 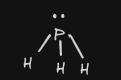 | P | InterMF: DIP DIP |
| Column 1 | Column 2 | Column 3 | Column 4 | Column 5 | Column 6 | Column 7 | Column 8 |
| # of Valence Electrons | Chemical Formula | Lewis Dot Diagram (do all atoms except H have an octet?) | Number of Domains off Central Atom | Name of VSEPR Shape | Redraw Lewis Structure in its Correct Shape (if needed) | Polarity of Molecule P or NP | Strongest Intermolecular Forces present |
| 8 | CH4 | 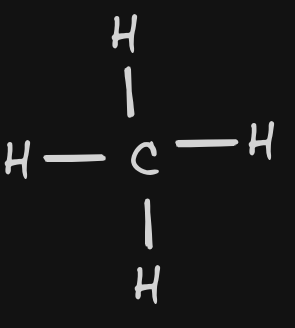 | Bonding: 4 Non-Bonding: 0 | tetrahedral | polar | InterMF:Dipole Dipole | |
| 10 | HCN | 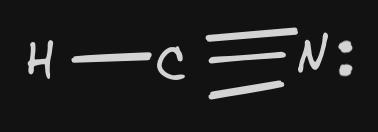 | Bonding: 2 Non-Bonding: 0 | linear | polar | InterMF:H bonding | |
| 14 | CH3Cl | 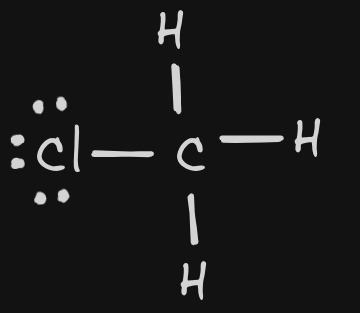 | Bonding: 4 Non-Bonding: 0 | tetrahedral | polar | InterMF:Dipole Dipole | |
| 12 | O2 |  | Bonding: 1 Non-Bonding: 2 ? linear. | linear | nonpolar | InterMF:LDF | |
| 12 | C2H2 |  | Bonding: 3 ? Non-Bonding: 0 | linear | nonpolar | InterMF:Dipole Dipole |
Analysis:
-
Describe a covalent bond in terms of:
-
Type of elements it contains: nonmetals
-
How do the electrons acquire the octet (transferring, sharing…)? sharing
-
Calculate the electronegativity difference between the 2 atoms & state the bond type (ionic, polar covalent, nonpolar covalent, metallic)
EN Difference Bond Type
-
Na-Cl 2.7 Ionic
-
S-O .7 Polar
-
F –F 0 Nonpolar
-
A. Define the term dipole. A molecule with 2 poles
B. Draw the dipole ONLY over the polar covalent bonds.
- A molecule having two such charges or poles.`
P NP P
H-S Cl-Cl C-Br
→ ||||||||| →
-
What are the 2 criteria needed to predict the polarity correctly? HINT: Look at Polarity Summary Chart
electronegativity ( .41 to 1.69 ) and shape
-
Draw the following structures in the box. Identify the shape & the polarity of the molecule.
-
HI shape: linear
polarity: polar

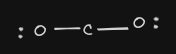
- CO2 shape: linear
polarity: nonpolar