L1: Solution Terminology & How and why Solutions form
A solution is made up of two parts:
- Solute ( the substance that is dissolved ,usually in minority if both are in the same state )
- Solvent ( the substance that does the dissolving, usually in majority if both are in the same state )
Properties of a Solution:
- Solute is evenly dispersed throughout the solvent
- Solute particles are so small that they pass through the pores of filter paper
- Solute particles are small enough to remain suspended in solvent all the time ( 1 phase is observed )
A compound is soluble if the forces of attraction between the ions with water are greater than the forces of attraction between the positive and negative ions. Otherwise it is insoluble.
Water molecules are polar and their opposite ends of partial charge are attracted to the charges of the ions in an ionic compound. Water carries away ions if the intermolecular forces between the water and the ion are stronger than the intermolecular forces between the ions. These free floating ions in the solution allow electricity to be conducted.
Substances that produce free floating charges when dissolved in water are called electrolytes.
When molecules separate from other molecules but free floating charges are not produced, the solution CANNOT conduct electricity. These are called nonelectrolytes.

Dissociation Equations: Breaking up electrolytes of ionic compounds in water
- Break the ionic compound apart into the positive and negative ions
- Leave polyatomic ions intact ( including the subscript within the polyatomic ion )
- All subscripts not within a polyatomic become coefficients
- include charges on dissociated ions
L2 Factors that Affect Solubility & reading Solubility Curves
Unsaturated - not full, we can add more solute to the solvent and it will dissolve. visually you can see no solid at the bottom saturated - full, no more solute can be dissolved, visually you can see solid at the bottom super-saturated - has more solute dissolved than would make a saturated solution at room temperature. there is no visual for this.
A super saturated solution can be seeded. this solution at room temperature that has beyond the amount of solid it can dissolve it will eventually become saturated when disturbed.
Higher temperature the solution, the more solid can be dissolved. Usually a direct relationship: as temperature increases, solubility of a solid increases. Pressure does not affect solubility.
The higher temperature a solution, the less gas can dissolve.
Inverse relationship: as temperature increases, the solubility of a gas decreases.
Pressure can also affect the solubility of a gas in a liquid.
Henry’s law: as pressure above a liquid increases, the solubility of a gas within a liquid will increase as well.
Above the line in a solubility curve means saturated
On the line means saturated
below the line means unsaturated
if it is above the line and it is understood that solute has been added and it all dissolved, it is supersaturated.
L3 Molarity Calculations
Concentration is the amount of solute in a given amount of solution
Dilute: Small amount of solute compared to solvent
Concentrated: large amount of solute compared to solvent
Molarity is a concentration unit that uses moles of the solute instead of mass of the solute.
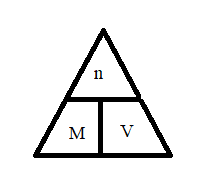
M ( molarity ) = moles of solute / Liters of solution
L4 How to make a solution and dilution Calculations
Blueprint for answering: Add _____ g of _____ ( solute ) to a volumetric flask. Then add small amounts of water while stirring until _____ ml of solution has been reached.
In order to find, use molarity triangle:
A Dilution is a technique designed to make a concentrated solutoin into a more dilute solution. The moles of the solute never change during the process of dilution. You do not need to change the volume into liters. Just make sure that both volume amounts are in the same units. Look for the “OF”: The molarity and volume connected by “of” must stay together
M1V1 = M2V2
if it says adds anywhere in there, add the added stuff to the m2v2 section
VOCAB
Miscible: mixable in all proportions Solute: Substance dissolved in another substance Soluble: capable of being dissolved in water Properties of a solution: solute evenly dispesed, particles small enough to pass through pores of filter paper, particles small enough to remain suspended in solvent all the time nonelectrolyte: Compound that doesn’t conduct imiscible: Cannot be mixed, forms 2 distinct things. electrolyte: Medium containing ions that are electrically conductive endothermic: the solvent and solute need to break intermolecular forces 9 REQUIRES ENERGY ) Exothermic: new intermolecular forces are formed between miexd solents & solute ( releases energy )